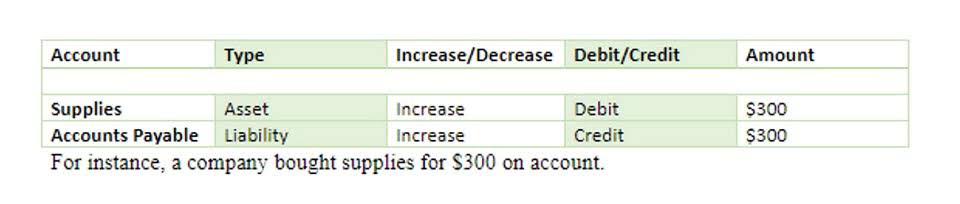
As such, many business owners are now trying to identify any weaknesses within their business and fiscal operations and make the necessary changes to ensure they can survive a significant income loss. In the US, patents protect companies for a period of time when they manufacture or create a unique design or product. Once a patent expires, competitors can begin using the original design, recipe, or process to create their comparable product. As long as customer and client needs are being met, stoppages aren’t always a concern.
Advantages of Going Concern Concept
According to this principle, financial statements are prepared, assuming the company intends to continue operations for the foreseeable future and has no motive or need to shut down. Economic uncertainty has been prevalent in global markets over the last several years due to many unexpected macro events – from COVID-19 and the related supply chain disruptions to international conflicts and rising interest rates. While some companies thrive from uncertainty, others may see their financial performance, liquidity and cash flow projections negatively impacted. These vulnerabilities continue to shine a bright light on management’s responsibility for a going concern assessment.
Should the auditor discover the going concern assumption to be untrue, what follows?
This enables stakeholders to analyze trends, assess performance, and evaluate the company’s financial health over time. Creditors are a significant stakeholder group concerned with the long-term viability of a debtor in bankruptcy proceedings. When faced with uncertainty about Medical Billing Process a company’s future as a going concern, they might prefer liquidation to recover their debts rather than waiting for an uncertain outcome from reorganization efforts. In contrast, equity holders, such as shareholders and bondholders, may prefer the business to continue operating under a new plan to preserve their investment’s value.
The Going Concern Assumption in Financial Reporting
The entity is already in breach of its agreed overdraft and the bank has refused to renew the borrowings. The entity has also been unsuccessful in applying to other financial institutions for re-financing. It is highly unlikely that the entity will be successful in renewing or re-financing the $10m borrowings and, in such an event, the directors will have no alternative but to cease to trade.

Trend analysis examines financial statements over time to identify patterns or anomalies, such as revenue growth or expense shifts, that may signal opportunities or risks. For example, steady revenue growth with stable expenses reflects effective management. The auditor should not use conditional language regarding the existence of substantial doubt about the entity’s ability to continue as a going concern. The going concern assumption is one of the three fundamental accounting assumptions, along with the accrual basis and consistency assumptions.

The Role of Management Representation Letters in Audits
For example, fixed assets like equipment and buildings are recorded at their original cost rather than their current market value. Companies must also inform investors and creditors about possible going concern issues. For instance, if a company is facing financial difficulties from an excessive debt burden or is facing a large liability lawsuit that could bankrupt the company, management must mention these cautions in the financial statement notes. Potential investors have the right to know if going concern the company’s going concern or longevity is in question. If nothing about the going concern is mentioned in the financial statementnotes, it is assumed that the company faces no threatening financial problems. This is an important concept to financial accounting because many other accounting principles are based on the assumption that companies will not cease to exist at the end of a period.
Enhancing Audit Quality Through Auditor Diversity

However, generally accepted auditing standards (GAAS) do instruct an auditor regarding the consideration of an entity’s ability to continue as a going concern. Generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) deal with the issue of going concern and its assessment. GAAP provides examples of the events and conditions that may indicate reason for substantial doubt that a company can continue to operate as a going concern.
Vedantu’s Instasolve – 12 Months – 24 hours Unlimited Instant Doubt Solving
Under Step 1, management determines whether events and conditions raise substantial doubt about the company’s ability to continue as a going concern. Under IFRS Standards, financial statements are prepared on a going concern basis, unless management intends or has no realistic alternative other than to liquidate the company or stop trading. Unlike US GAAP, there is no liquidation basis of accounting under IFRS; when a company determines it is no longer a going concern, it does not prepare financial statements on a going concern basis. However, in our view, there is no general dispensation from the measurement, recognition and disclosure requirements of the Standards in this case, and these requirements are applied in a manner appropriate to the circumstances. The principle encourages management to accounting assess and address potential risks that could threaten the company’s ability to continue operations.

Subscribe to the IFRS® Perspectives Newsletter
- Upon filing for bankruptcy, a business transitions from being an operating entity to entering a legal process managed by the court.
- Going concern refers to a company that can meet its obligations and continue operations indefinitely, while liquidation indicates the sale or dissolution of a business’s assets.
- Also, the transaction should involve all the related assets that facilitate income generation.
- Creditors evaluate a company’s ability to meet debt obligations based on its going concern status.
- It assumes that the entity will continue to remain in business for the foreseeable future.
Here, too, there arises a requirement for the company to disclose any uncertainties related to its ability to continue its operation in its financial reports. The company might consider putting all its assets at liquidation value, which may be less than their original cost. This would result in a change in the set of financial statements, thus offering an improved image of the financial condition of the company.
